This section overviews the main activities carried out within the wave energy sector. It provides a general description of the sector, summarises the most important wave energy projects, and highlights the main characteristics of wave energy. It also includes a bibliography review to various wave energy research areas, and a summary of relevant European research projects.
“Utilization of wave energy will contribute to the world´s future sustainable energy supply.
It can provide electricity, drinking water and other products at competitive prices, creating jobs and reducing dependence on fossil fuels. It will reduce the world energy sector´s carbon emission, whilst minimising impacts on marine environments” [Ocean Energy Systems, 2012]. Read more
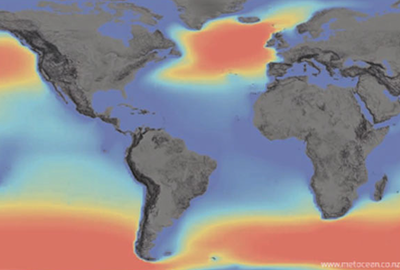
Wave energy is one of five energies available in the oceans.
The energy in the waves is a concentrated form of solar energy: the sun heats the atmospheres unevenly and the differences in pressure create currents in the atmospheres (known as winds), and winds blowing over the ocean surface transfer their energy to the oceans in the form of waves. Read more
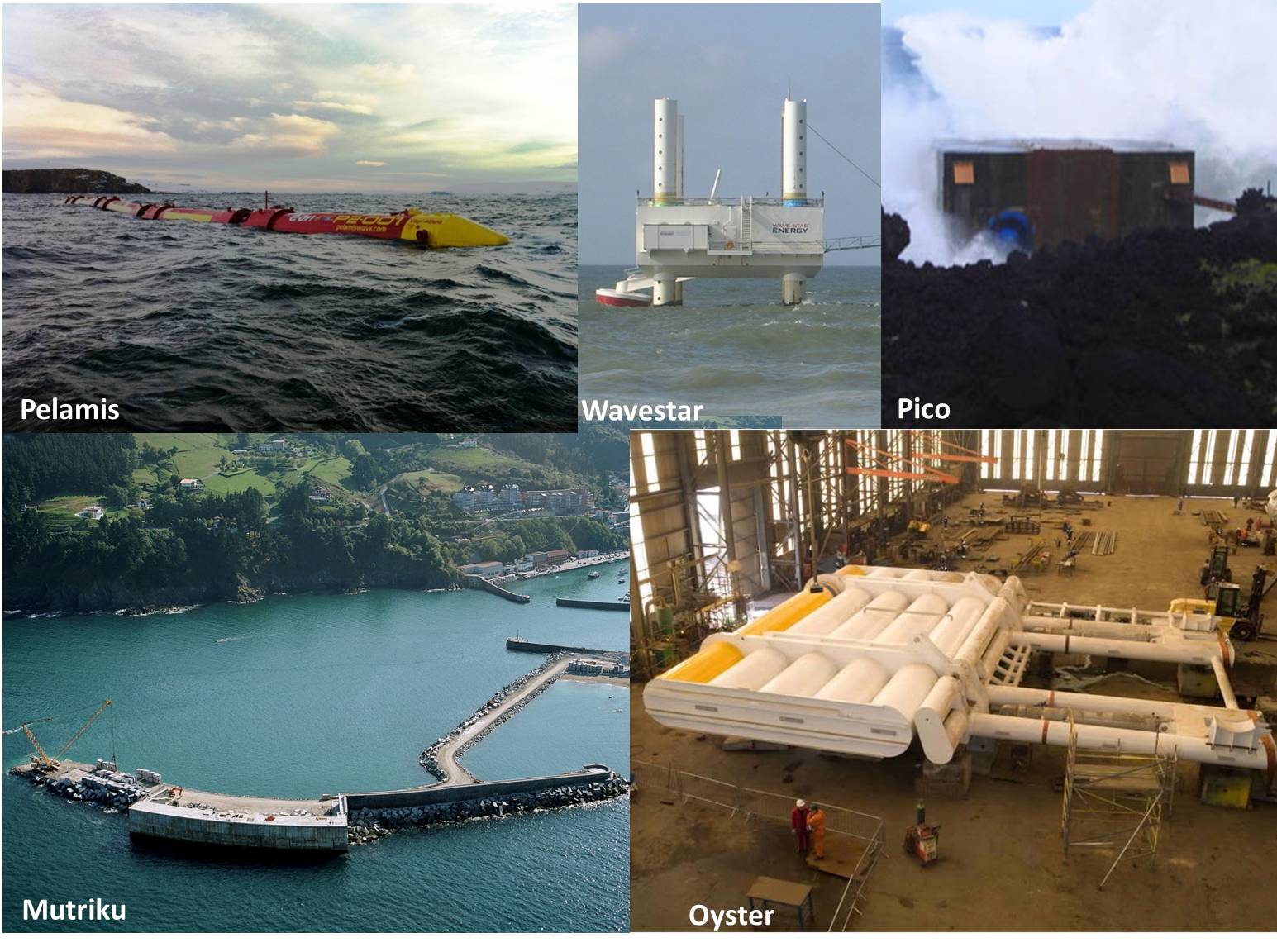
Wave energy developments are characterised by numerous inventions.
There are many success stories in the wave energy sector, as well as failures

Harnessing the energy in the waves is full of opportunities to current energy systems.
Nevertheless, the way ahead for wave realisation is beset with difficulties, particularly related to testing in real seas, due to the characteristics of ocean waves and to the costs. Read more

There is extensive literature on wave energy.
A brief review of references is presented, that describes the wave energy resource, technologies, conversion systems and developments.

In 1991 the European Commission (EC) included wave energy in its Research and Development (R&D) programmes (OES, 2009) and since then a large number of projects have been funded.